The Texas Historical Commission (THC) is the state agency for historic preservation, tasked with protecting a variety of architectural, archeological, and cultural landmarks.
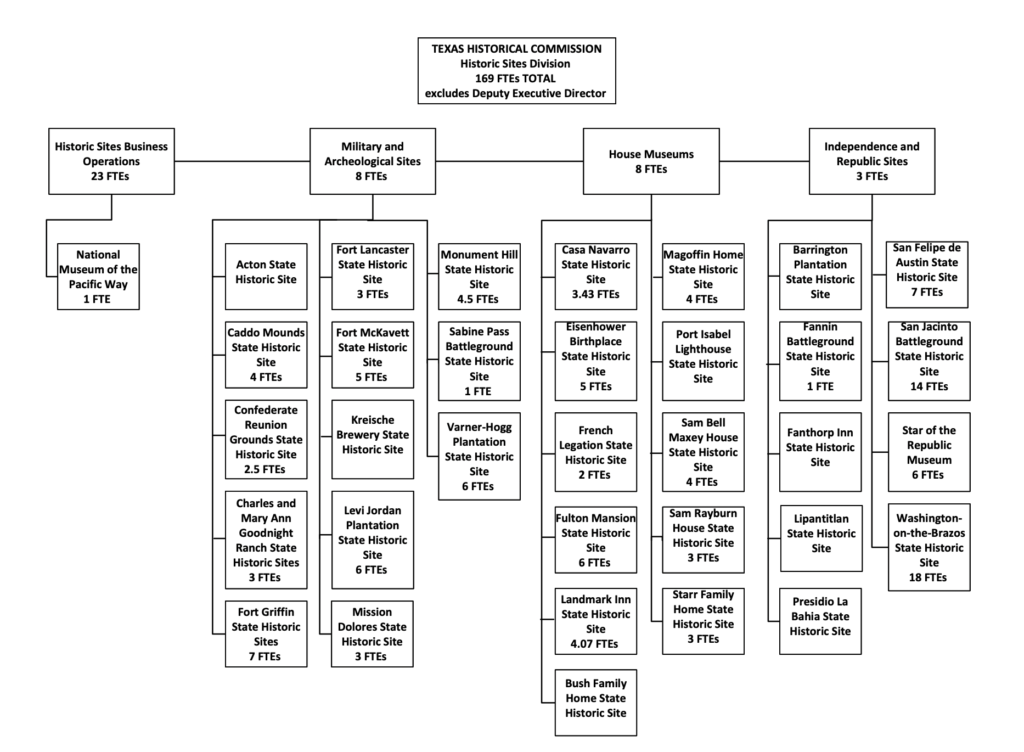
THC operates 36 historic sites including museums, military forts, and archeological sites. Among these are Caddo Mounds, the Dwight D. Eisenhower Birthplace, Fannin Battleground, and the site of the signing of the Texas Declaration of Independence at Washington-on-the-Brazos.
THC also administers the state’s historical marker program, which maintains about 17,000 markers across the state, and the statewide heritage tourism program. Established in 1998, the program is based around 10 thematic driving trails established decades earlier by the Texas Department of Transportation at the request of Governor John Connally.
The commission’s Archeology Division issues permits for all archeological investigations on public land. The commission regulates archeological digs on public land and also works with property owners to save archeological sites on private land.






Agency Structure
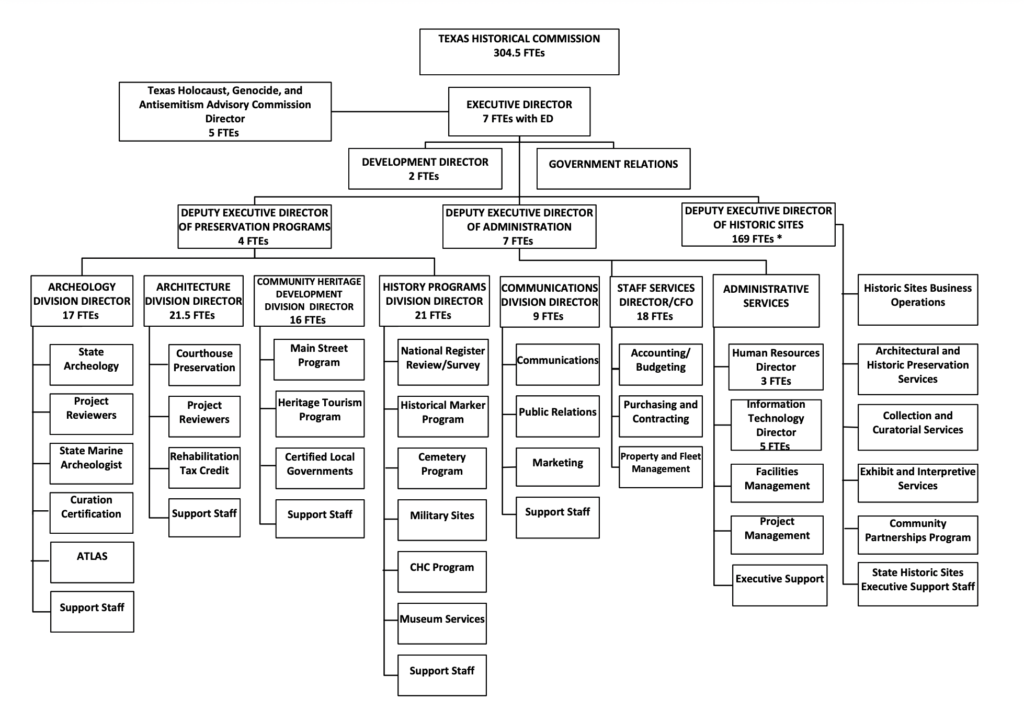
The Texas Historical Commission is composed of 15 citizen members appointed by the governor to staggered six-year terms. Agency employees include archeologists, architects, historians, economic development and tourism specialists, and urban planners.
The commission employs about 470 personnel.
History
The Texas Legislature established the agency in 1953 as the Texas State Historical Survey Committee. The Legislature changed the agency’s name to the Texas Historical Commission in 1973, and gave it expanded role, including broader educational responsibilities.
Budget
The Texas Historical Commission is funded through a constitutionally-dedicated share of sales tax on sporting goods.



